Reetu | Jun 29, 2022 |
![Decisions taken in 47th Meeting of the GST Council [Read Official Press Release]](/cdn-cgi/image/fit=contain,format=webp,gravity=auto,metadata=none,quality=80,width=1200,height=730/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/47th-Meeting-of-the-GST-Council.jpg)
Decisions taken in 47th Meeting of the GST Council [Read Official Press Release]
The GST Council’s 47th meeting was held in Chandigarh on 28th and 29th June, 2022 under the chairmanship of the Union Finance & Corporate Affairs Minister Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman.
The GST Council has, among other things, recommended the following amendments to GST law and procedure as well as adjustments to the GST rates on the sale of goods and services:
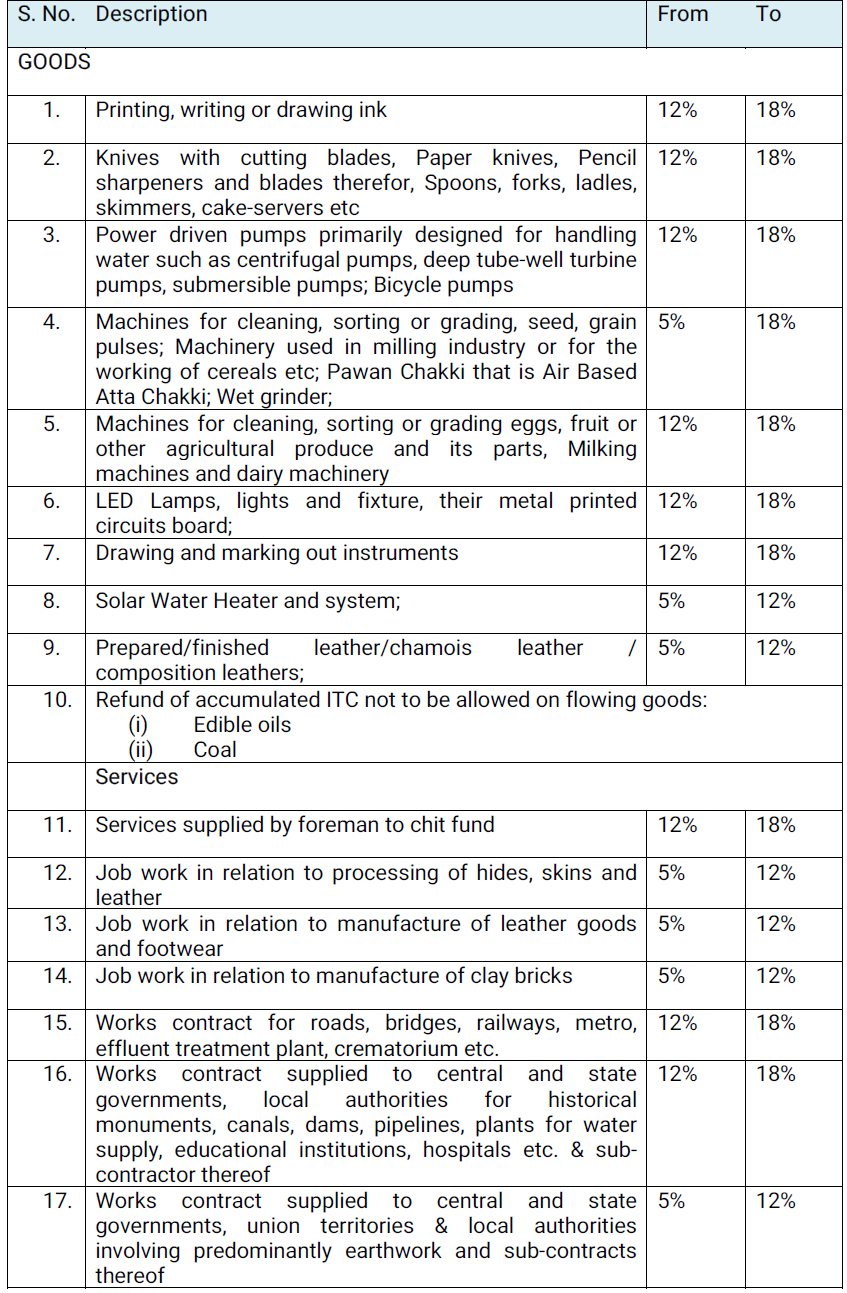
C.1 GST has previously been exempted from some foods, cereals, etc. when they are not branded or the right to the brand has been waived. It has been suggested that the Legal Metrology Act’s pre-packaged and pre-labeled retail packs, such as curd, lassi, and butter milk, be excluded from the scope of the exemption.
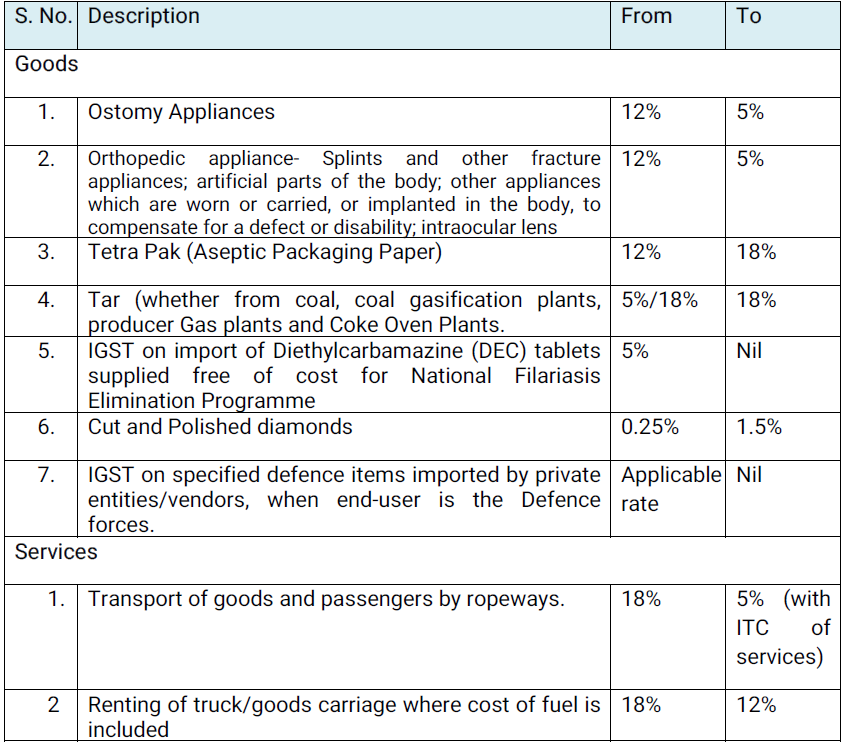
C.2 In case of the following goods, exemption from GST will be withdrawn:
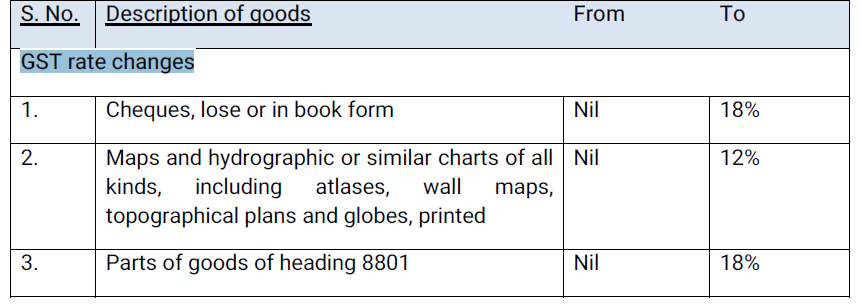
C.3 In case of the following goods, the exemption in form of a concessional rate of GST is being rationalized:

C.4 In case of Services, following exemptions are being rationalized:

The Council instructed the Group of Ministers on Casino, Racetrack, and Online Gaming to re-examine the issues in its mandate based on new information from States and deliver a report as soon as possible.
E1. Goods
E2. Clarification in relation to GST rate on Services
1. In-principal approval for relaxation in the provisions for suppliers making supplies through E-Commerce Operators (ECOs)
I. Waiver of requirement of mandatory registration under section 24(ix) of CGST Act for person supplying goods through ECOs, subject to certain conditions, such as-
II. Composition taxpayers would be allowed to make intra-State supply through e-commerce operators subject to certain conditions.
The Council’s Law Committee will determine the specifics of the plan. The plan would be tentatively implemented starting on January 1, 2023, pending readiness on the portal and from ECOs.
2. Amendment in formula prescribed in sub-rule (5) of rule 89 of CGST Rules, 2017 for calculation of refund of unutilized Input Tax Credit on account of inverted rated structure
a. Change to the rule 89(5) refund calculation formula to account for ITC use on account of inputs and input services for payment of output tax on inverted rated supplies in the same ratio as ITC has been accessed on inputs and input services throughout the specified tax year. The taxpayers who receive ITC for input services would also benefit from this.
3. Amendment in CGST Rules for handling of pending IGST refund claims:
a. Refund requests for export of products may occasionally be blocked or withheld if the exporter is determined to be a dangerous exporter who needs verification by GST officials or if there is a violation of the Customs Act’s restrictions.
b. It has been suggested that rule 96 of the CGST Rules be amended to allow such IGST refund claims to be transmitted via the portal in a system-generated GST RFD-01 form for processing by the relevant GST authorities. Such exporters would benefit from the prompt resolution of such IGST refund claims following proper GST officer verification.
4. Re-credit of amount in electronic credit ledger to be provided in those cases where erroneous refund amount sanctioned to a taxpayer on account of accumulated ITC or on account of IGST paid on zero rated supply of goods or services, in contravention of rule 96(10) of the CGST Rules, is deposited by him along with interest and penalty, wherever applicable. A new FORM GST PMT-03Ais introduced for the same.
This will enable the taxpayers to get re-credit of the amount of erroneous refund, paid back by them, in their electronic credit ledger.
5. Clause (c) of section 110 and section 111 of the Finance Act, 2022 to be notified by Central Government at the earliest
These provisions relate to-
a. retrospective amendment in section 50(3) of CGST Act, with effect from 01.07.2017,to provide that interest will be payable on the wrongly availed ITC only when the same is utilized;
b. amendment in sub-section (10) of section 49 of CGST Act to provide for transfer of balance in electronic cash ledger of a registered person to electronic cash ledger of CGST and IGST of a distinct person
It has also been suggested to clarify the regulations governing how interest is calculated under Section 50 of the CGST Act. This will clear up any confusion over how interest is calculated and allow the balances in the CGST and IGST cash ledgers to be transferred between different people, boosting the taxpayers’ liquidity and cash flow.
6. Waiver of late fee for delay in filing FORM GSTR-4 for FY 2021-22 and extension of due date for filing FORM GST CMP-08 for Q1 of FY 2022-23:
a. To extend the waiver of late fee under section 47 for delay in filing FORM GSTR-4 for FY 2021-22 by approximately four more weeks, i.e. till 28.07.2022 (The existing waiver is for the period from 01.05.2022 till 30.06.2022)
b. To extend the due date of filing of FORM GST CMP-08 for the 1st quarter of FY 2022-23 from 18.07.2022 to 31.07.2022.
Additionally, GSTN has been requested to swiftly address the concern regarding the negative balance in the Electronic Cash Ledger that some of the composition taxpayers are experiencing.
7. Present exemption of IGST on import of goods under AA/EPCG/EOU scheme to be continued and E-wallet scheme not to be pursued further.
8. Issuance of the following circulars in order to remove ambiguity and legal disputes on various issues, thus benefiting taxpayers at large:
a. Clarification on the topic of requesting a refund under an inverted duty structure where the supplier is providing goods in accordance with a special notification.
b. Clarification on several matters pertaining to the application of the CGST Act’s demand and penalty clauses in relation to transactions using fraudulent invoices
c. Clarification on mandatory furnishing of correct and proper information of inter-State supplies and amount of ineligible/blocked Input Tax Credit and reversal thereof in return in FORM GSTR-3B.
d. Clarification in respect of certain GST related issues:
i. Clarification on the issues pertaining to refund claimed by the recipients of supplies regarded as deemed export;
ii. Clarification on various issues relating to interpretation of section 17(5) of the CGST Act;
iii. Clarification on the issue of perquisites provided by employer to the employees as per contractual agreement;
iv. Clarification on utilization of the amounts available in the electronic credit ledger and the electronic cash ledger for payment of tax and other liabilities.
9. Exemption from filing annual return in FORM GSTR-9/9A for FY 2021-22to be provided to taxpayers having AATO upto Rs. 2 crores.
10. To clarify that there is no necessity to reverse input tax credit for exempted supply of Duty Credit Scrips by the exporters, Explanation 1 after Rule 43 of the CGST Rules shall be revised.
11. UPI & IMPS to be provided as an additional mode for payment of Goods and Services Tax to taxpayers under Rule 87(3) of CGST Rules.
12. In respect of refunds pertaining to supplies to SEZ Developer/Unit, an Explanation to be inserted in sub-rule (1) of rule 89 of CGST Rules to clarify that “specified officer” under the said sub-rule shall mean the “specified officer” or “authorized officer”, as defined under SEZ Rules, 2006.
13. Refund of unused Input Tax Credit on account of Electricity Export is provided by an amendment to the CGST Rules. This would make it easier for energy exporters to request a refund of ITC that was used on zero-rated shipments.
14. Supplies from Duty Free Shops (DFS) at international terminal to outgoing international passengers to be treated as exports by DFS and consequential refund benefit to be available to them on such supplies. Rule 95A of the CGST Rules, Circular No. 106/25/2019-GST dated 29.06.2019 and related notifications to be rescinded accordingly.
1. Provision for automatic revocation of suspension of registration in cases where suspension of registration was done by the system under Rule 21A(2A) of CGST Rules, for non-compliance in terms of clause (b) or clause (c) of sub- section (2) of section 29[continuous non-filing of specified number of returns], once all the pending returns are filed on the portal by the taxpayer. (Amendmentinrule21A)
2. Proposal for comprehensive changes in FORM GSTR-3B to be placed in public domain for seeking inputs/suggestions of the stakeholders.
3. Time period from 01.03.2020 to 28.02.2022 to be excluded from calculation of the limitation period for filing refund claim by an applicant under section 54 and 55 of CGST Act, as well as for issuance of demand/ order (by proper officer) in respect of erroneous refunds under section 73 of CGST Act. Further, limitation under section 73 for FY 2017-18 for issuance of order in respect of other demands linked with due date of annual return, to be extended till 30th September, 2023.
C. The Council has decided to constitute a Group of Ministers to address various concerns raised by the States in relation to constitution of GST Appellate Tribunal and make recommendations for appropriate amendments in CGST Act.
D. The GST Council approved ad-hoc apportionment of IGST to the extent of Rs. 27,000 crores and release of 50% of this amount, i.e. Rs. 13,500 crores to the States.
E. The GoM on IT Reforms, inter alia, recommended that the GSTN should put in place the AI/ML based mechanism to verify the antecedents of the registration applicants and an improved risk-based monitoring of their behavior post registration so that non-compliant tax payers could be identified in their infancy and appropriate action be taken so as to minimize risk to exchequer.
Note: The recommendations of the GST Council have been presented in this release containing major item of decisions in simple language for information of all stakeholders. The same would be given effect through relevant Circulars/ Notifications/ Law amendments which alone shall have the force of law.
In case of any Doubt regarding Membership you can mail us at contact@studycafe.in
Join Studycafe's WhatsApp Group or Telegram Channel for Latest Updates on Government Job, Sarkari Naukri, Private Jobs, Income Tax, GST, Companies Act, Judgements and CA, CS, ICWA, and MUCH MORE!"