Deepak Gupta | Jul 9, 2017 |

Job work in GST, Treatment of Jobwork in GST, Impact of Goods and Service Tax (GST) on Job work, Job Work under GST, Transitional Provisions Under Job Work, GST Impact on Jobwork, Job Work Definition in GST, GST Job Work, Job Work
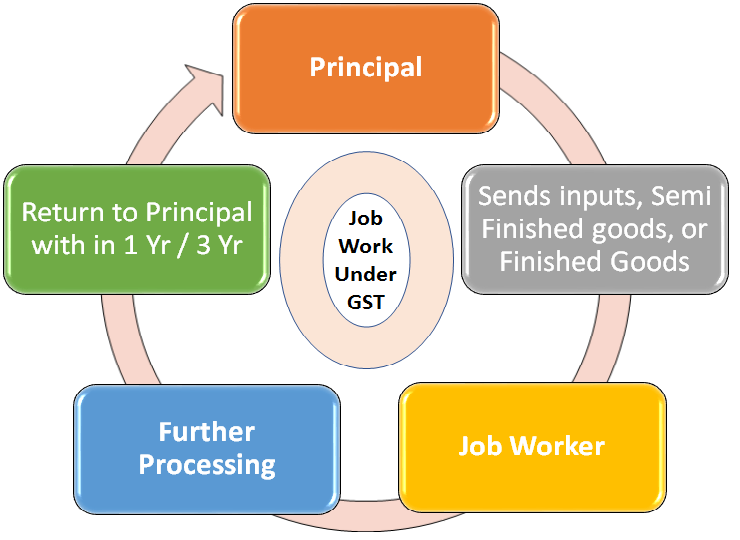
Job-work sector constitutes a significant industry in Indian economy. The term Job-work itself explains the meaning. It is processing of goods supplied by the principal. The concept of job-work already exists in Central Excise, wherein a principal manufacturer can send inputs, semi finished goods or Finished Goods to a job worker for further processing. Many facilities, procedural concessions have been given to the job workers as well as the principal supplier who sends goods for job-work. The whole idea is to make the principal responsible for meeting compliances on behalf of the job-worker on the goods processed by him (job-worker), considering the fact that typically the job-workers are small persons who are unable to comply with the discrete provisions of the law.
The GST Act makes special provisions with regard to removal of goods for job-work and receiving back the goods after processing from the job-worker without the payment of GST. The benefit of these provisions shall be available both to the principal and the job worker.
A manufacturer may send out his goods to a job worker for initial process, intermediate process, assembly, packing or any other completion process and later supply such goods to its customers or use in any other manufacturing process accompanied by its own. Section 2(68) of the CGST Act, 2017 defines job-work as any treatment or process undertaken by a person on goods belonging to another registered person . The one who does the said job would be termed as job worker . The ownership of the goods does not transfer to the job-worker but it rests with the principal. The job worker is required to carry out the process specified by the principal on the goods.

Certain facilities with certain conditions are offered in relation to job-work, some of which are as under:
a) A registered person (Principal) can send inputs/ capital goods under intimation and subject to certain conditions without payment of tax to a job-worker and from there to another job-worker and after completion of job-work bring back such goods without payment of tax. The principal is not required to reverse the ITC availed on inputs or capital goods dispatched to job-worker.
b) Principal can send inputs or capital goods directly to the job-worker without bringing them to his premises and can still avail the credit of tax paid on such inputs or capital goods.
c) However, inputs and/or capital goods sent to a jobworker are required to be returned to the principal within 1 year and 3 years, respectively, from the date of sending such goods to the job-worker.
d) After processing of goods, the job-worker may clear the goods to-
(i) Another job-worker for further processing
(ii) Dispatch the goods to any of the place of business of the principal without payment of tax
(iii) Remove the goods on payment of tax within India or without payment of tax for export outside India on fulfillment of conditions.
The facility of supply of goods by the principal to the third party directly from the premises of the jobworker on payment of tax in India and likewise with or without payment of tax for export may be availed by the principal on declaring premise of the job-worker as his additional place of business in registration. In case the job-worker is a registered person under GST, even declaring the premises of the job-worker as additional place of business is not required.
Before supply of goods to the job-worker, the principal would be required to intimate the Jurisdictional Officer containing the details of the description of inputs intended to be sent by the principal and the nature of processing to be carried out by the job-worker. The said intimation shall also contain the details of the other job-workers, if any.
The inputs or capital goods shall be sent to the jobworker under the cover of a challan issued by the principal. The challan shall be issued even for the inputs or capital goods sent directly to the job-worker. The challan shall contain the details specified in Rule 10 of the Invoice Rules.
The responsibility for keeping proper accounts for the inputs or capital goods shall lie with the principal.
Section 19 of the CGST Act, 2017 provides that the principal (a person supplying taxable goods to the jobworker) shall be entitled to take the credit of input tax paid on inputs sent to the job-worker for the job-work. Further, the proviso also provides that the principal can take the credit even when the goods have been directly supplied to the job-worker without being brought into the premise of the principal. The principal need not wait till the inputs are first brought to his place of business.
Procedures for claiming Input Credit on Job Work
A. Goods purchased may be send to job worker in the following manner:
ITC will be allowed in both of the above mentioned cases.
B. Effective date for goods send depends on place of business:
C. The goods send must be received back by the principal manufacture within the following period:
from date of being send out or receipt by job worker depending on place of business from where goods are send- Refer point- A & B
D. In case goods are not received within 3 yrs (capital goods)and 1 yr (Input Goods) such goods will be treated as supply from effective date and tax will be payable on such deemed supply and the challan issued will be treated as an invoice for such supply

Input Tax Credit Rules:
Rule 10: Conditions and restriction in respect of inputs and capital goods sent to the job worker
Rule 10(1): The inputs or capital goods shall be sent to the job worker under the cover of a challan issued by the principal, including where the inputs or capital goods are sent directly to job-worker.
Rule 10(2): The challan issued by the principal to the job worker shall contain the details specified in rule Invoice.8:
Rule 10(3): The details of challans in respect of goods dispatched to a job worker or received from a job worker during a tax period shall be included in FORM GSTR-1 furnished for that period.
Rule 10(4): If the inputs or capital goods are not returned to the principal within the time stipulated in section 143, the challan issued under sub-rule (1) shall be deemed to be an invoice for the purposes of this Act.
As per section 19 of the CGST Act, 2017, inputs and capital goods after processing shall be returned back to principal within one year or three years respectively of their being sent out. Further, the provision of return of goods is not applicable in case of moulds and dies, jigs and fixtures or tools supplied by the principal to job-worker.
Inputs, as such, or partially processed inputs which are sent to a job-worker prior to introduction of GST under the provisions of existing law [Central Excise] and if such goods are returned within 6 months from the appointed day [i.e. the day on which GST will be implemented] no tax would be payable. If such goods are not returned within prescribed time, the input tax credit availed on such goods will be liable to be recovered.
If the manufactured goods are removed, prior to the appointed day, without payment of duty for testing or any other process which does not amount to manufacture, and such goods are returned within 6 months from the appointed day, then no tax will be payable. For the purpose of these provisions during the transitional period, the manufacturer and the job-worker are required to declare the details of such goods sent/received for job-work in prescribed format GST TRAN-1, within 90 days of the introduction of GST
Raw Material/ Inputs Removed for Job Work and Returned on or after GST Roll-Out
Where goods have been removed from a factory for further processing to a job worker prior to the GST applicable date, i.e. goods were removed under current tax regime however received back after GST roll-out;
Similarly in case of Semi-finished or Finished goods, a job worker is not required to pay tax under GST, if such goods are returned to original manufacturer s place of business within a period of 6 months from the GST applicable date.
If the said goods are not returned within the period specified in this sub-section, the input tax credit shall be liable to be recovered in accordance with the provisions of clause (a) of sub-section (8) of section 142
Every person to whom the provisions of section 141 apply shall, within sixty days of the appointed day, submit an application electronically in FORM GST TRAN-1, specifying therein, the stock or, as the case may be, capital goods held by him on the appointed day details of stock or, as the case may be, capital goods held by him as a principal at the place/places of business of his agents/branch, separately agent-wise/branch-wise.
The provisions relating to job work have been adopted in the IGST Act as well as in SGST / UTGST Act from CGST Act and therefore job-worker and principal can be located either in same State or in same Union Territory or in different States or Union Territories and applicable in the similar fashion.

Only the Registered Persons can avail the provisions of the scheme Sec 143 (1) of CGST Act
The provisions require that goods (Inputs or Capital Goods) can only be removed to job worker s place under intimation to the concerned authorities Sec 143 (1) of CGST Act
Any inputs or capital goods can be sent without payment of tax, to a job worker for job-work Sec 143 (1) of CGST Act
The term inputs, for the purposes of job work, input includes intermediate goods arising from any treatment or process carried out on the inputs by the principal or the job worker Sec 143 (1) of CGST Act Explanation
Goods from the job worker subsequently can be send to another job worker and likewise Sec 143 (1) of CGST Act
Such job work provisions subject to condition that Inputs be brought back within one year Sec 143 (1) (a) of CGST Act
In case of capital goods, other than moulds and dies, jigs and fixtures, or tools be brought back within Three Years Sec 143 (1) (a) of CGST Act
After completion of job work, such goods may be sent out from the place of business of a job worker on payment of tax within India, or with or without payment of tax for export, as the case may be. Sec 143 (1) (b) of CGST Act
For sending the goods after job work from the place of business of the job-worker, either the Job Worker be Registered or the Principal should declare the job workers place as his additional place of business Sec 143 (1) (b) of CGST Act
Responsibility for accountability lies with the Principal Sec 143(2) of CGST Act
Inputs sent to Job Worker not received back within one year Considered as Deemed Supply on the day when the said inputs were sent out Sec 143(3) , Sec 19(3) of CGST Act
Capital Goods sent to Job Worker not received back within three years Considered as Deemed Supply on the day when the said CGs were sent out Sec 143(4) , Sec 19(6) of CGST Act
Inputs & Capital Goods can be sent directly from other supplier to the Job worker without being first brought to his place of business inferred from Sec 19(2) & Sec 19(5) of CGST Act
ITC allowed on inputs sent to Job worker by principal Sec 19(1) of CGST Act
ITC allowed even if inputs directly sent to the Job worker Sec 19(2) of CGST Act
ITC allowed on Capital goods sent to Job worker by principal Sec 19(4) of CGST Act
ITC allowed even if capital goods directly sent to the Job worker -Sec 19(5) of CGST Act
Moulds and dies, jigs and fixtures, or tools sent out to a job-worker are not required to be received back by the Principal Excluded from the Job Work Provisions Sec 19(7) of CGST Act,
Waste and Scrap generated at Job worker may be supplied by the job worker directly from his place of business on payment of tax by Job Worker if such job worker is registered, or by the principal, if the job worker is not registered Section 143(5) of CGST Act
Credit on inputs which got consumed during job work not separately identifiable consumables cannot be received back by the principal condition of receiving back the goods after job work cannot be satisfied.
Provisions relating to Job Work are not applicable to exempted or non-taxable goods
Job work Charges by job worker shall be treated as supply of service and accordingly GST is applicable in case the threshold limit is crossed Schedule II (3) Treatment or process: Any treatment or process which is applied to another person s goods is a supply of services.
The Job worker need to register in case he crosses the threshold limit or his supplies are across the states (inter state) Sec 22(1) & Sec 24 of CGST Act
The goods of principal directly supplied from the job worker s premises will not be included in the aggregate turnover of the job worker. It will be included in the aggregate turnover of the principal. However, the value of goods or services used by the job worker for carrying out the job work will be included in the value of services supplied by the job worker. Sec 22(4) Explanation ii of CGST Act
Pursuant to Section 143 (5) of the CGST Act, 2017, waste generated at the premises of the job-worker may be
supplied directly by the registered job-worker from his place of business on payment of tax or such waste may
be cleared by the principal, in case the job-worker is not registered.
The goods of principal directly supplied from the job worker s premises will not be included in the aggregate turnover of the job worker.
This Article has been shared by CS Kirandeep Kaur. She can be reached @ [email protected]
In case of any Doubt regarding Membership you can mail us at [email protected]
Join Studycafe's WhatsApp Group or Telegram Channel for Latest Updates on Government Job, Sarkari Naukri, Private Jobs, Income Tax, GST, Companies Act, Judgements and CA, CS, ICWA, and MUCH MORE!"