Deepak Gupta | Mar 24, 2019 |
Critical analysis of SO CALLED Composition Scheme for service providers
GST Council in its Meeting held on 10 January 2019 took a major decision to bring in composition scheme for services. The press release of the meeting itself stated as follows:
Extract of Press Release 3. Composition Scheme for Services: A Composition Scheme shall be made available for Suppliers of Services (or Mixed Suppliers) with a Tax Rate of 6% (3% CGST +3% SGST) having an Annual Turnover in the preceding Financial Year up to INR 50 lakhs. 3.1 The said Scheme shall be applicable to both Service Providers as well as Suppliers of Goods and Services, who are not eligible for the presently available Composition Scheme for Goods. |
Therefore, everyone was waiting for the modalities to be rolled out for the composition scheme for services. The modalities were rolled out vide Notification No. 02/2019-Central Tax (Rate), dated 07 March 2019 (hereinafter referred as the scheme notification) for the commonly called composition scheme for services on 07 March 2019. This article tries to decipher and analyse the scheme and raise issues relevant to the scheme at relevant places.
1.) Is this really a composition scheme or a tax rate on services with no input tax Credit
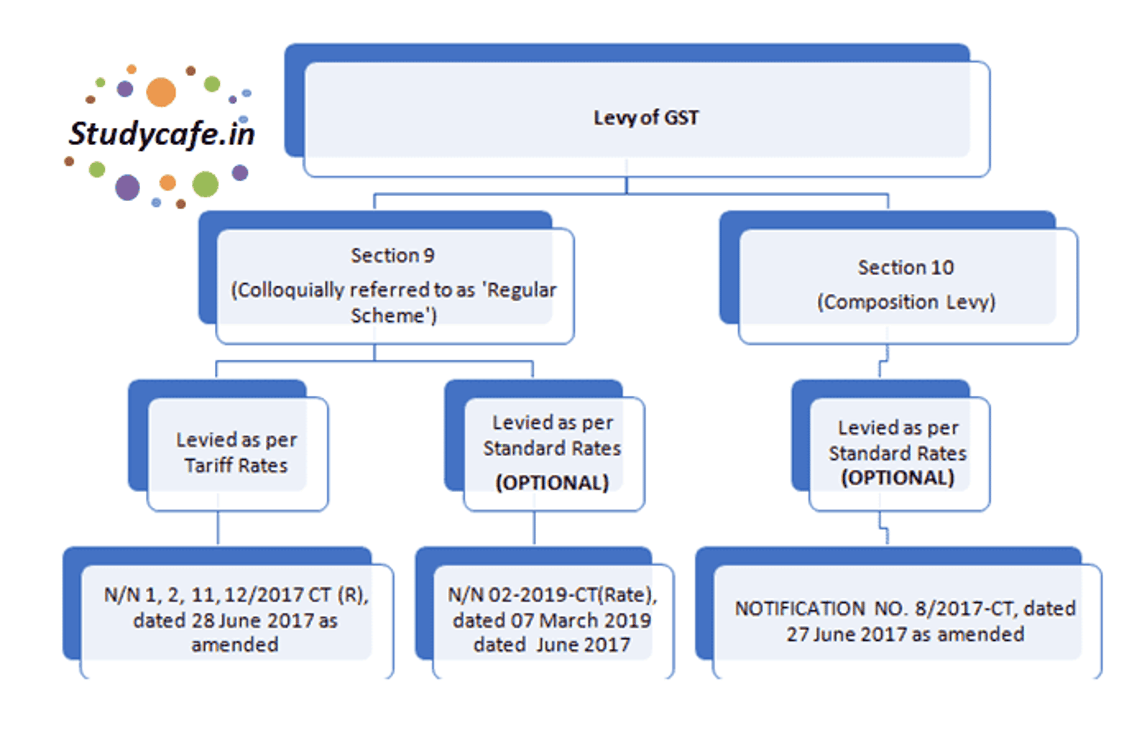
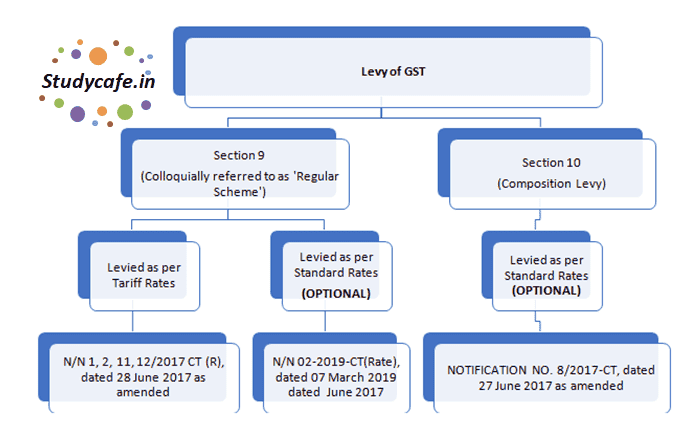
The scheme notification been issued u/s 9(1), u/s 11(1) and u/s 16(1) of the CGST Act, 2017 whereas notification for composition scheme 08/2017-Central Tax dated 27thJune 2017 was issued u/s 10(1) of CGST Act, 2017.
Therefore, it is clear that the present scheme is not a composition scheme for the service providers as normally understood in common parlance subsequent to the meeting of the GST Council. Had the scheme notification been issued u/s 10 of CGST Act, 2017, it would have been treated as a composition scheme for service providers.
One of the questions which arise is why notification 02/2019-Central Tax (Rate), dated 07 March 2019 has been issued u/s 9(1), u/s 11(1) and u/s 16(1) of the CGST Act, 2017. In the article going ahead, we would be discussing the same at relevant places.
2.) What is the impact of scheme under Notification No. 02/2019-Central Tax (Rate), 07 March 2019 not being a composition scheme u/s 10 of CGST Act, 2017
The impact of scheme notification being issued u/s 9(1), u/s 11(1) and u/s 16(1) of the CGST Act, 2017 and not being issued u/s 10 of CGST Act would be the fact that the scheme would not per se have the attributes and the conditions mentioned u/s 10 of CGST Act, 2017 read with Rule 5 of CGST Rules 2017. Therefore, tax levied and collected under the scheme notification would not be composition levy in lieu of tax u/s 10 and other conditions like Time limit to opt in or out of composition scheme, Turnover limit, Ineligibility to Input Tax Credit, denial of outward Inter State Supply etc. would have to be provided for in the notification separately. Consequently, none of the forms for opting in and opting out for composition scheme and claim of Input Tax Credit on opting out of composition scheme would be applicable.
Thus, in a nutshell, scheme would have to be a complete code by itself which notification no. 02/2019-Central Tax (Rate), dated 07 March 2019 has sought to laid down and although in common parlance (but not technically) one may call the scheme as a composition scheme for service providers but in effect it has no link whatsoever with the provisions of section 10 of CGST Act, 2017.
Further, conditions as set out in scheme notification might be similar to the ones present in Section 10 read with Rule 5 of CGST Rules, 2017 but then since the scheme notification has not been issued in Section 10, therefore it was required that the notification had to prescribe the code in entirety itself.
Therefore, taxpayers opting for the scheme would be governed by the conditions as set out in the scheme notification and not be conditions as set out in Section 10 of CGST Act, 2017 read with rule 5 of CGST Rules, 2017.
One more important aspect is that the scheme notification no. 02/2019-Central Tax (Rate), dated 07 March 2019 gives an option to registered supplier to opt for scheme although modus operandi to exercise this option has not been provided by this scheme notification.
3.) Notification only prescribes rate of tax on the intra-State supply of goods or services or both
The scheme notification at the outset provides that
Central Government, on the recommendations of the Council, and on being satisfied that it is necessary in the public interest so to do, hereby notifies that the central tax, on the intra-State supply of goods or services or both
Firstly, the tax rate provided in the scheme notification is for supply of goods or services or both. Secondly, rate prescribed is only for intra state supply of goods or services or both. The reason for the same is that Condition 1(iv) of the Notification puts a bar on making outward supply of goods or services or both. Since there is bar on making any inter-state outward supply, therefore a person opting for the scheme would only be making intra state supply of goods or services and hence notification only prescribes rate for intra state supply.
4.) Condition 1-Conditions for opting for Scheme as set out in Notification No. 02/2019-Central Tax (Rate), dated 07 March 2019-
a.) Condition 1(i)-Supplies are made by a registered person whose aggregate turnover in the preceding financial year was INR 50 lakhs or below
The term aggregate turnover has been defined u/s 2(6) of CGST Act, 2017 to include all taxable and exempt supplies by a person having the same Permanent Account Number, to be computed on all India basis. Therefore, turnover of the person having the same PAN on all India Basis has to be INR 50 lakhs or below in the previous year. Therefore, if a person has multiple branches in different states, then turnover of all his branches should be fifty lakh or below in the previous year on an aggregate basis.
Next question is what happens for a person who was not registered in the previous year. There might be two situations in such case-
– Person might have started a new business in the current year and thus would not have any turnover in the previous year- Such person would be eligible to opt for the scheme as his turnover was less than 50 Lakhs in the previous year.
– Person could have been exclusively dealing in exempted goods or services in the previous year and thus was not required to be registered- Such person would be eligible if his turnover of exempted goods or services or both was less than INR 50 Lakhs but if his turnover exempted goods or services or both was more than INR 50 Lakhs (although not required to be registered under GST as dealing exclusively in exempted goods), then he would not be eligible to opt for the scheme.
b.) Condition 1(ii)-Supplies are made by a registered person who is not eligible to pay tax under sub-section (1) of section 10 of the said Act:
Importantly, the condition sets out that the registered person shall not be eligible to pay tax u/s 10(1) of CGST Act.
Section 10 of CGST Act, 2017 read with Rule 5 of CGST Rules, 2017 sets out provisions for the conditions to be satisfied by a person to be eligible to opt for composition scheme. Therefore, it could be possible that a person might satisfy all conditions as set out therein but still does not opt for composition scheme. Therefore, it is pretty clear that eligibility and opting are two different actions and cannot be held synonym to each other. Now lets consider scenarios have been listed as below:
– Situation-1: Eligible to pay tax u/s 10(1) of CGST Act, 2017 but not opted to pay tax therein (as discussed earlier)-:
– Situation-2: Not Eligible to pay tax u/s 10(1) of CGST Act, 2017 therefore did not opt to pay tax therein-:
Since the scheme notification uses the term registered person should not be eligible to pay tax u/s 10(1), therefore a person who is eligible u/s 10(1) but has not opted (Situation-1 as narrated above) would not be able to opt for the scheme as set out in notification 02/2019-Central Tax (Rate), dated 07 March 2019. Only person who are falling in Situation-2 as narrated above would be able to opt for the scheme.
In a nutshell, if a person wants to opt for the scheme notified vide 02-2019-Central Tax (Rate) then following would be the process:
– Want to opt for the scheme notified vide 02-2019-Central Tax (Rate) dated 07 March 2019 – Yes
– Whether Eligible to pay tax u/s 10(1) of CGST Act, 2017- If yes then either opt for Composition Scheme u/s 10(1) of CGST Act, 2017 or wait till the person becomes ineligible to opt to pay tax under composition scheme u/s 10(1) of CGST Act.
– Whether Ineligible to pay tax u/s 10(1) of CGST Act, 2017-Yes, then opt for the scheme notified vide 02-2019-Central Tax (Rate) dated 07 March 2019.
Therefore, an absurd scenario has been created wherein every person opting to pay tax under the scheme notification 02/2019-Central Tax (Rate), dated 07 March 2019 should either be ineligible to pay tax u/s 10(1) of CGST Act, 2017 at that time or if he is not ineligible therein, then he would have to first opt to pay tax under composition scheme u/s 10(1) of CGST Act or would have to wait till he becomes ineligible to opt to pay tax under composition scheme u/s 10(1) of CGST Act, and then once he becomes ineligible to pay tax therein then only he can opt to pay tax under the scheme notification 02/2019-Central Tax (Rate), dated 07 March 2019.
c) Condition 1(iii): -Supplies are made by a registered person who is not engaged in making any supply which is not leviable to tax under the CGST Act
Registered person should not be engaged in making supply which is not leviable to tax under the Act. Supply not leviable to tax has been termed as non-taxable supplies u/s 2(78) of CGST Act, 2017. Supplies of following goods are not leviable under GST
Alcoholic liquor for human consumption
Petroleum crude,
High speed diesel,
Motor spirit (commonly known as petrol),
Natural gas and
Aviation turbine fuel.
d) Condition 1(iv): – Supplies are made by a registered person who is not engaged in making any inter-State outward supply
Registered person should not be engaged in making any inter-state outward supply. The condition might seem to be a simple one and an obvious one but needs to checked very carefully. The condition casts restriction on making any inter-state outward supply which covers both taxable and exempt supply and supply of goods or services or both. Therefore, there should not be any inter-state outward supply of exempted goods or services or both also.
e) Condition 1(v): – Supplies are made by a registered person who is neither a casual taxable person nor a non-resident taxable person
Registered person should neither be a casual taxable person and nor a non-resident taxable person. The term casual taxable person and non-resident taxable person has been defined u/s 2(20) and 2(77) of CGST Act, 2017 respectively.
f) Condition 1(vi): – Supplies are made by a registered person who is not engaged in making any supply through an electronic commerce operator who is required to collect tax at source u/s 52
Registered person should not be engaged in making any supply through an electronic commerce operator who is required to collect tax at source u/s 52. It would be pertinent to highlight that although registered person engaged in making any supply through an electronic commerce operator who is required to collect tax at source u/s 52 is barred from opting the scheme, but the person who is himself an electronic commerce operator is not barred from opting the scheme.
g) Condition 1(vii): – Supplies are made by a registered person who is not engaged in making supplies of the goods falling under Tariff item, subheading, heading or Chapter 21050000, 21069020 and 24
Supplier should not be engaged in making supplies of the goods specified below falling under Tariff Item, subheading, heading or chapter as detailed out:
Tariff item, sub-heading, heading or Chapter | Description |
2105 00 00 | Ice cream and other edible ice, whether or not containing cocoa |
2106 90 20 | Pan masala |
24 | All goods, i.e. Tobacco and manufactured tobacco substitutes |
It would be apt to highlight here that notifications – Central Tax (Rate), dated 07 March 2019 casts restriction supplier making any making supplies of the goods falling under Tariff item, subheading, heading or Chapter as narrated above however, section 10(2)(e) of CGST Act, 2017 only casts restriction on opting for composition for the manufacturer of such goods. Therefore, Section 10(2)(e) casts restriction only on manufacturers but Notification 02/2019-Central Tax (Rate), dated 07 March 2019 casts restriction upon both manufacturer and traders as well. Therefore, the condition as set out in Notification 02/2019-Central Tax (Rate), dated 07 March 2019 is a much wider one than section 10(2)(e) of CGST Act, 2017.
5. Condition 2-: Persons having multiple registrations on Permanent Account Number
Where more than one registered person has same Permanent Account Number, issued under the Income Tax Act, 1961(43 of 1961), tax on supplies by all such registered persons would have to be paid under the scheme notification. Registered persons having same Permanent Account Number can be in the same state or in different states. Hence, if a person is registered in Gujarat as well as Rajasthan, then both registrations would have to pay tax under Notification No. 02/2019-Central Tax (Rate), dated 07 March 2019. There can not be a situation wherein one registration is paying tax under the scheme notification and other one is paying tax otherwise. This condition exists on similar lines to the one prescribed u/s 10(2) of the CGST Act, 2017.
6. Condition 3: Restriction on collection of Tax and Input Tax Credit
Registered person shall not collect any tax from recipient on supplies made by him nor shall he be entitled to any credit of input tax.
a) Supplier can not collect any tax from recipient: Scheme notification casts a restriction on the supplier to collect tax from the recipient. Therefore, amount to be paid as tax under this notification would have to be paid by the supplier himself without being collected from the recipient.
The next question is on what amount such tax would be collected and whether amount collected from the recipient would be deemed as inclusive of taxes or otherwise. Supposedly, a person has a receipt of INR 20 lakhs and GST has to be paid @ 6%. Whether such person can pay GST @ 6% treating amount collected as inclusive of such amount i.e. INR 20 Lakh/1.06*.06 or 6% has to be paid at Rs 20 Lakh i.e. Rs 20 Lakh*6%. Since the notification casts restriction on any amount being collected from the recipient as tax, therefore 6% would have to be paid on 20 Lakh and it cannot be deemed that Rs 20 Lakh is inclusive of the tax to be paid.
Further, it would be apt here to highlight that in case of restaurants or passenger transportation services, although the rate has been prescribed at 5% but there is no restriction on the amount being collected from the recipient. This is an additional restriction being placed on the supplier which is not present in case of similar tax rate being prescribed without entitlement of input tax credit.
b.) Supplier not eligible to any credit of input tax: Scheme notification casts a restriction on the entitlement of input tax credit of the supplier. The supplier would not be eligible to claim any input tax credit against the tax payable on the supplies made by him.
Requirement to issue notification u/s 16(1) of CGST Act: The very fact that the scheme is not covered u/s 10 and scheme notification casts restriction on entitlement of input tax credit of supplier, therefore notification has been issued u/s 16(1) of CGST Act, 2017. Had the notification not been issued u/s 16(1), it would not have been possible to restrict the entitlement of input tax credit of the supplier against the tax payable by him.
7. Condition 4: Registered person to issue Bill of Supply instead of tax invoice
Registered person would be required to issue bill of supply as referred to in clause (c) of sub-section (3) of section 31 of the said Act with particulars as prescribed in rule 49 of Central Goods and Services Tax Rules. The reason behind the restriction stems from the fact that as the supplier cannot collect tax from recipient, therefore instead of tax invoice he would be required to issue bill of supply.
The moot question here is whether a notification issued under sub-section (1) of section 9, subsection (1) of section 11, sub-section (1) of section 16 of CGST Act, 2017 can require a person to issue Bill of Supply without referring to Section 31 of the CGST Act, 2017. It would not have been possible in the present scheme and therefore to remove said anomaly, a Removal of Difficulty order No. 3/2019-Central Tax, dated 08 March 2019 was issued to clarify that provisions of section 31(3)(c) of CGST Act shall apply to a person paying tax under notification No. 2/2019- Central Tax (Rate) dated 07 March 2019.
8. Condition 5: Registered person to mention at top of bill of supply: – taxable person paying tax in terms of notification No. 2/2019-Central Tax (Rate) dated 07.03.2019, not eligible to collect tax on supplies
The condition is similar to the one mentioned in Section 10 of CGST Act, 2017 read with Rule 5 of CGST Rules, 2017. A person opting to pay composition levy in lieu of the tax payable has to mention “composition taxable person, not eligible to collect tax on supplies” at the top of the bill of supply issued by him. In the scheme notification, taxable person opting to pay tax under the given notification has to mention at top of bill of supply: – taxable person paying tax in terms of notification No. 2/2019-Central Tax (Rate) dated 07.03.2019, not eligible to collect tax on supplies.
9. Condition 6: Registered person shall be liable to pay tax at the rate of six percent on all outward supplies notwithstanding any other notification issued under sub-section (1) of section 9 or u/s 11 of said Act
Registered person opting to pay tax under this notification shall be liable to pay tax at the rate of six percent on all outward supplies specified in column (1) notwithstanding any other notification issued under sub-section (1) of section 9 or u/s 11 of said Act. This is one of the most onerous condition prescribed in this notification. This requires the registered person to pay tax at the rate of 6% on all outward supplies whether they are taxable or exempted from the levy of tax. For e.g. Lets take following scenarios for better understanding:
Scenario | Particulars | Tax Liability |
Scenario-1: | Taxable Supplies of Goods: INR 15 Lakh Exempted Supplies of Services: INR 10 Lakh | INR 1.5 Lakh |
Scenario-2: | Taxable Supplies of Goods: INR 25 Lakh | INR 1.5 Lakh |
Scenario-3: | Exempted Supplies of Services: INR 25 Lakh | INR 1.5 Lakh |
Thus, it is immaterial whether supplier is supplying exempted or taxable goods or services or both, once opted for payment of tax under this notification, he would be liable to pay tax at the rate of 6% on all supplies irrespective of their nature i.e. taxable or exempt.
This brings us to another question i.e. whether such tax at the rate of 6% is payable on Non-GST Supplies also. In such a case Condition 1(iii) of scheme notification as discussed above clearly spells out the fact that any person engaged in making supplies which are not leviable to tax would not be eligible to opt to pay tax under the given notification. Therefore, such situation would never arise wherein a person is engaged in making supplies not leviable to tax under the Act and who has opted to pay tax under this notification.
a) How notification overrides exemption given to goods or services from levy of Tax under GST
The next question arises is that supposedly a particular service or goods are exempted from levy of tax. Now scheme notification No. 02/2019-Central Tax (Rate), dated 07 March 2019 requires the registered person to pay tax even on the exempted goods or services or both irrespective of any other notification issued under sub-section (1) of section 9 or u/s 11 of said Act.
The very fact that the scheme notification requires registered person to pay tax even on otherwise exempted supplies, thus it was required that such notification had to be issued u/s 11 of the CGST Act, 2017 to override all other exemption notification. Therefore, to allow to override any other exemption given previously to goods or services or both from levy of tax for persons opting to pay tax under this notification; scheme notification 02/2019-Central Tax (Rate), dated 07 March 2019 has been issued under subsection (1) of section 11 along with sub-section (1) of section 9 and sub-section (1) of section 16 of the CGST Act, 2017. Thus, a supply otherwise exempted from tax vide any other notification has been made leviable to tax under this notification overriding any other previous exemption for the persons opting to pay tax under this notification.
b). Whether supplier would also be liable to pay tax on supplies made by him which are liable to reverse charge and tax is payable by the recipient:
The moot question now arises is whether supplier would be liable to pay tax on supplies made by him which are liable to reverse charge and tax is payable by the recipient. The condition provides that registered person opting to pay central tax at the rate of three percent under this notification shall be liable to pay central tax at the rate of three percent on all outward supplies specified in column (1).
Section 2(83) defines the outward supply as below:
“outward supply” in relation to a taxable person, means supply of goods or services or both, whether by sale, transfer, barter, exchange, licence, rental, lease or disposal or any other mode, made or agreed to be made by such person in the course or furtherance of business;
All Outward Supplies specified in Column 1 of the notification are First supplies of goods or services or both upto an aggregate turnover of INR 50 lakhs made on or after the 1st day of April in any financial year, by a registered person.
Therefore, on a conjoint reading it transpires that registered person opting to pay tax at the rate of 6% under the scheme notification shall be liable to pay tax at the rate of 6% on first supplies of goods or services or both upto an aggregate turnover of INR 50 lakhs made on or after the 1st day of April in any financial year.
Since this condition provides that tax is payable on all outward supplies upto an aggregate turnover of INR 50 lakhs and no specific exclusions have been made for outward supplies liable for payment of tax under reverse charge from aggregate turnover under this notification, therefore it appears that tax is payable @ 6% on the supplies on which tax is payable under reverse charge mechanism by the recipient.
The next question arises whether in such case tax would also be payable by the recipient. It seems so because liability of the recipient is not affected by this notification and notifications in which liability of the recipient has been created have not been override or have been carved out as an exception through this notification. Therefore, liability of the recipient remains unaffected under those notifications and a new liability has been created under this notification on the supplier for such supplies.
However, further clarity in this regard would be welcome.
10. Condition 8-: Registered person shall be liable to pay tax under reverse charge on inward supplies u/s 9(3) or 9(4) of CGST Act
Registered person opting to pay tax under this notification shall be liable to pay tax on inward supplies on which he is liable to pay tax under sub-section (3) or, as the case may be, under sub-section (4) of section 9 of said Act at the applicable rates. The condition is similar to the one prescribed for the persons opting to pay composition levy in lieu of tax payable u/s 9(1) of CGST Act, 2017 wherein they are required to pay tax under reverse charge on inward supplies u/s 9(3) and 9(4) of the CGST Act, 2017.
The issue now arises is what was the need of casting the said condition in this notification or without this condition, whether liability of the registered person to pay tax u/s 9(3) and 9(4) would have been affected.
Composition levy u/s 10(1) is in lieu of tax payable u/s 9(1) of CGST Act, 2017. Section 10(1) starts with a non-obstinate clause Notwithstanding anything to the contrary contained in this Act. Therefore, section 10(1) was required to be made subject to provisions of section 9(3) and 9(4) so as to maintain liability of the registered person u/s 9(3) and 9(4) of CGST Act, 2017 irrespective of the payment of composition levy in lieu of tax payable u/s 9(1) of CGST Act, 2017. But since the scheme notification does not have a similar overriding impact such as Section 10 of CGST Act, 2017, therefore such condition seems to be more clarificatory in nature.
The second question arises is why reference has been made only to Reverse charge payable u/s 9(3) and 9(4) and not for reverse charge under 5(3) and 5(4). Again, since the reference to liability of reverse charge u/s 9(3) and 9(4) is clarificatory in nature, therefore reference to section 5(3) and 5(4) was not required. Further, since the notification has been issued under the relevant provisions of CGST Act, 2017 therefore as such the levy u/s 5(1) read with 5(3) and 5(4) remains as unaffected.
Thus, reference to liability u/s 9(3) and 9(4) of CGST Act, 2017 seems to have been taken out from the scheme of composition levy u/s 10 of CGST Act, 2017 but, it seems more in the nature of clarification.
11. Condition 9-: The scheme would be applicable till supplies of goods or services or both upto an aggregate turnover of INR 50 lakhs made on or after the 1st day of April in any financial year, by a registered person
A person who has opted for the scheme would be able to continue in the scheme till first supplies of goods or services or both upto an aggregate turnover of INR 50 lakhs made on or after the 1st day of April in any financial year. Once the turnover crosses the threshold limit of Rs Fifty Lakh, then in such case he will have to opt out of the scheme.
The term aggregate turnover has been defined u/s 2(6) of CGST Act, 2017 to include all taxable and exempt supplies by a person having the same Permanent Account Number, to be computed on all India basis. Turnover of the person having the same PAN on all India Basis has to be INR 50 lakhs or below. Therefore, if a person has multiple branches in different states, then he will be eligible for the scheme till the turnover of all his branches is fifty lakh or below on an aggregate basis.
a) What is meant by first supplies of goods or services or both
Explanation to the notification classifies meaning of first supplies of goods or services or both in two categories i.e.
For the purposes of determining eligibility of a person to pay tax under this notification
Explanation to the notification clarifies that first supplies of goods or services or both shall, for the purposes of determining eligibility of a person to pay tax under this notification, include the supplies from the first day of April of a financial year to the date from which he becomes liable for registration under the Act.
For the purpose of determination of tax payable under this notification
Explanation to the notification clarifies that first supplies of goods or services or both shall, for the purpose of determination of tax payable under this notification shall not include the supplies from the first day of April of a financial year to the date from which he becomes liable for registration under the Act.
b) Whether a person who has obtained new registration can opt for the scheme:
Yes, subject to other conditions being satisfied, a person who has obtained a new registration can opt for payment of tax under the scheme notification. The question arises is that supposedly a person applied for registration when his turnover was Rs 19 Lakh. In such case how would be the limit of aggregate turnover of INR 50 lakhs would be worked out. Whether he would get an additional turnover of Rs fifty lakh for the purpose of determining eligibility or he would only get additional turnover of Rs 31 lakh and after that he would have to opt out of the scheme.
For the purpose of determining his eligibility to opt to pay tax under this notification, his turnover would include supplies from the first day of April of a financial year to the date from which he becomes liable for registration under the Act. Therefore, his turnover of Rs 19 Lakh would be includible for determining eligibility upto a limit of INR 50 lakhs and he would only get additional turnover of INR 31 Lakh to be under the scheme notification and after that he would have to opt out of the scheme.
c) How does a person who has obtained a new registration would pay tax under the scheme notification
Supposedly, a person has obtained a new registration and at that time his turnover was INR 19 lakhs. Now supposedly, he has opted for payment of tax under the scheme notification. The issue arises is whether he would be required to pay tax on the turnover of INR 19 lakhs or he would only be liable to pay tax on the remaining turnover upto the limit of INR 50 lakhs i.e. Rs 31 Lakh.
For the purpose of determination of tax payable under this notification, first supplies of goods or services or both shall not include the supplies from the first day of April of a financial year to the date from which he becomes liable for registration under the Act. Therefore, such person would only be liable to pay tax on the remaining turnover of Rs 31 Lakh and would not be required to pay tax on the initial Rs 19 Lakh.
12. Condition 10: Treatment of Value of supply of exempt services by way of extending deposits, loans or advances in so far as the consideration is represented by way of interest or discount for the purpose of determining of eligibility of scheme under the scheme notification and taxability thereof
Scheme notification provides that in computing aggregate turnover in order to determine eligibility of a registered person to pay tax under this notification, value of supply of exempt services by way of extending deposits, loans or advances in so far as the consideration is represented by way of interest or discount, shall not be taken into account.
Therefore, for the purpose of computing aggregate turnover in order to determine eligibility of a registered person to pay tax under this notification, value of supply represented by way of interest or discount would be excluded however for the purpose of payment of tax, the notification is silent and therefore tax would be leviable on the value of supply represented by way of interest or discount.
13. Notification is silent on Key Issues: Government neds to clarify at the earliest
The notification is silent on certain key which are as follows:
a) Registered person crosses the aggregate turnover in the FY INR 50 lakhs or violates any conditions required to be fulfilled to opt this scheme, then whether he will be entitled to take the credit on the remaining inputs and capital goods
Such situations have been catered by provisions of section 18(1)(c) of CGST Act, 2017 for the persons who have opted for composition scheme but subsequently become ineligible for the composition scheme, where he is entitled to take ITC through ITC-01 but no such provisions exist for this scheme.
b) Notification does not provide any time limit for opting in the scheme and opting out of the scheme:
The notification is silent upon the time limit available for opting in the scheme or opting out of the scheme.
c) Whether registered person opting to pay tax under this notification would be required to maintain books of accounts in a similar manner as required by the persons opting for composition scheme
No corresponding changes have been made in the provision relating to maintenance of books of accounts. Section 35 read with Rule 56, 57 and 58 regulate the provision for books of accounts. It can be observed that provisions relating to maintenance of books of accounts and records by persons registered under the composition scheme are relaxed w.r.t. stock, ITC, tax payable etc [for detail kindly read rule 56(2) and 56(4)] however no corresponding changes have been made for registered person opting to pay tax under this notification.
Rule 56(2): Every registered person, other than a person paying tax under section 10, shall maintain the accounts of stock in respect of goods received and supplied by him, and such accounts shall contain particulars of the opening balance, receipt, supply, goods lost, stolen, destroyed, written off or disposed of by way of gift or free sample and the balance of stock including raw materials, finished goods, scrap and wastage thereof.
Rule 56(4): Every registered person, other than a person paying tax under section 10, shall keep and maintain an account, containing the details of tax payable (including tax payable in accordance with the provisions of sub-section (3) and sub-section (4) of section 9), tax collected and paid, input tax, input tax credit claimed, together with a register of tax invoice, credit notes, debit notes, delivery challan issued or received during any tax period. |
In our opinion, there is a requirement to change the rules suitably in this regard. For example, being with the scheme opted under scheme notification, registered supplier can not take ITC then how a law can expect to maintain the records related to ITC.
d) Forms under GST law till date are not yet notified for the persons opting to pay tax under scheme notification
Till date no forms under GST law have been prescribed for the persons opting to pay tax under this notification. The scheme would be effective from 1st April 2019 and forms being released nearing the last date would again create hassles for the person opting to pay tax under this notification.
e) Treatment of balance ITC lying as on the date of opting to pay tax under this notification:
The notification is silent on the issue of treatment of ITC lying unutilized as on the date of opting to pay tax under thescheme notification.
f) Can we say that this once opted, means always applicable
Under this scheme GST will be levied at 6% on first supplies of goods or services or both (intra state) upto an aggregate turnover of INR 50 lakhs made on or after the 1st day of April in any financial year. However, notification is not clear whether scheme would have to be opted for each year separately or like composition scheme, once opted no need for renewal every year until the conditions are violated or specifically opted out.
Disclaimer: Authors of this article are not responsible for any decision taken based on this document. Our article is just an analysis and can always be challenged by divergent views and court of the law.
The Above article has been Authored by By Arpit Haldia and Vivek Laddha
Click Here to Buy CA INTER/IPCC Pendrive Classes at Discounted Rate
Tags : composition scheme gst, gst composition scheme rules, gst composition scheme for service providers, composition scheme limit, what is composition scheme, gst composition scheme turnover limit, gst composition scheme last date, gst composition rules
In case of any Doubt regarding Membership you can mail us at [email protected]
Join Studycafe's WhatsApp Group or Telegram Channel for Latest Updates on Government Job, Sarkari Naukri, Private Jobs, Income Tax, GST, Companies Act, Judgements and CA, CS, ICWA, and MUCH MORE!"