Reetu | Apr 7, 2021 |
FAQs on GST e-invoice System updated upto 31st March 2021
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is ‘e-invoicing’?
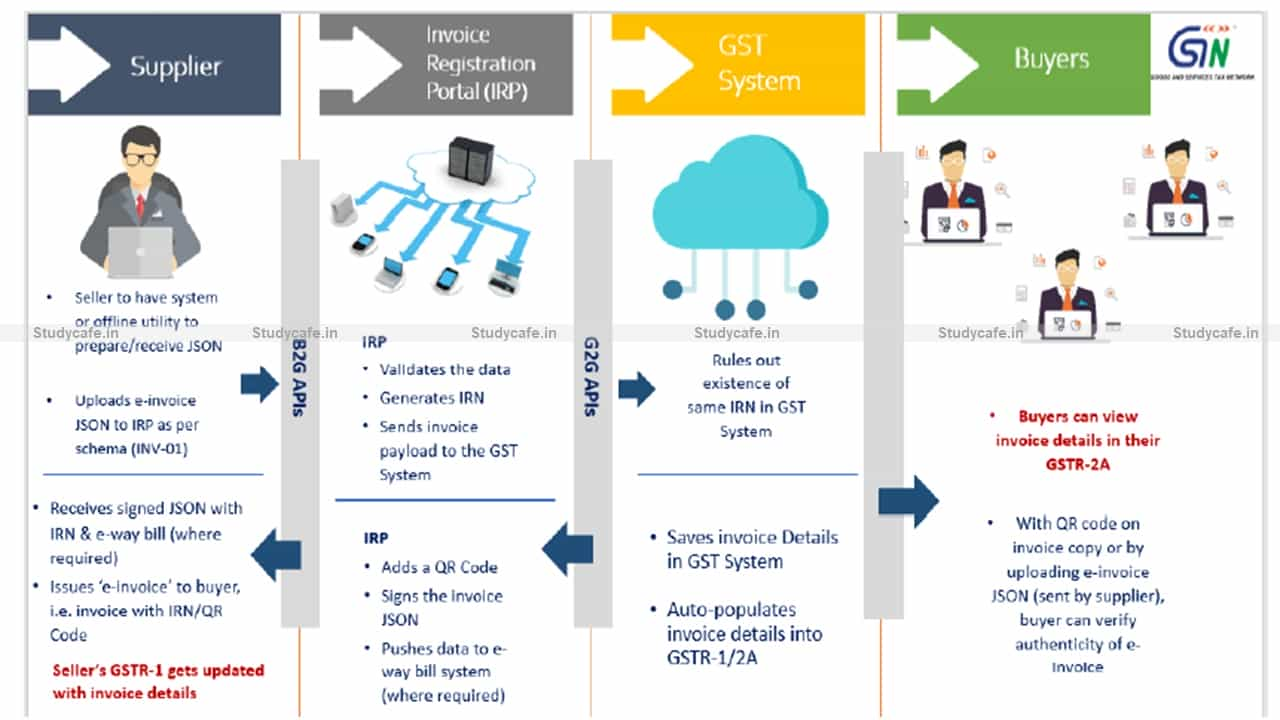
As per Rule 48(4) of CGST Rules, notified class of registered persons have to prepare invoice by uploading specified particulars of invoice (in FORM GST INV-01) on Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) and obtain an Invoice Reference Number (IRN).
After following above ‘e-invoicing’ process, the invoice copy containing inter alia, the IRN (with QR Code) issued by the notified supplier to buyer is commonly referred to as ‘e-invoice’ in GST.
Because of the standard e-invoice schema (INV-01), ‘e-invoicing’ facilitates exchange of the invoice document (structured invoice data) between a supplier and a buyer in an integrated electronic format.
Please note that ‘e-invoice’ in ‘e-invoicing’ doesn’t mean generation of invoice by a Government portal.
2. How is ‘e-invoicing’ different from present system?
There is no much difference indeed.
Registered persons will continue to create their GST invoices on their own Accounting/Billing/ERP Systems. These invoices will now be reported to ‘Invoice Registration Portal (IRP)’. On reporting, IRP returns the e-invoice with a unique ‘Invoice Reference Number (IRN)’ after digitally signing the e-invoice and adding a QR Code. Then, the invoice can be issued to the receiver (along with QR Code).
A GST invoice will be valid only with a valid IRN.
3. For which businesses, e-invoicing is mandatory?
For Registered persons whose aggregate turnover (based on PAN) in any preceding financial year from 2017-18 onwards, is more than prescribed limit (as per relevant notification), e-invoicing is mandatory.
4. What are the legal provisions governing e-invoice?
Below notifications were issued on e-invoice:
| Notification No. (Central Tax) | Key Contents |
| 68/2019 Dt. 13-12-2019 69/2019 Dt. 13-12-2019 70/2019 Dt. 13-12-2019 |
(4) The invoice shall be prepared by such class of registered persons as may be notified by the Government, on the recommendations of the Council, by including such particulars contained in FORM GST INV-01 after obtaining an Invoice Reference Number by uploading information contained therein on the Common Goods and Services Tax Electronic Portal in such manner and subject to such conditions and restrictions as may be specified in the notification. (5) Every invoice issued by a person to whom sub-rule (4) applies in any manner other than the manner specified in the said sub-rule shall not be treated as an invoice. (6) The provisions of sub-rules (1) and (2) shall not apply to an invoice prepared in the manner specified in sub-rule (4). Notified 10 Common Goods and Services Tax Electronic Portals for the purpose of preparation of invoice in terms of rule 48 (4) Notified registered person, whose aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds one hundred crore rupees, as a class of registered person who shall prepare invoice in terms of sub-rule (4) of rule 48 of the said rules in respect of supply of goods or services or both to a registered person; notification to come into force from the 1st day of April, 2020 (This notification superseded by 13 of 2020 Dt. 21-3-2020) |
| 2 of 2020 Dt. 1-1-2020 | Substituted Form GST INV-1 as e-invoice schema (Schema further amended vide Notification 60/2020 Dt. 30-7-2020) |
| 13 of 2020 Dt. 21-3-2020 (in supersession of 70/2019 Dt. 13-12-2019) |
(Further amended by 61/2020 Dt. 30-7-2020) |
| 60/2020 Dt. 30-7-2020 |
|
| 61/2020 Dt. 30-7-2020 70/2020 Dt. 30-9-2020 72/2020 Dt. 30-9-2020 73/2020 Dt. 01.10.2020 |
Notified a special procedure for taxpayers for issuance of e-Invoices in the period 01.10.2020 – 31.10.2020 |
| 88/2020 Dt. 10.11.2020 05/2021 Dt. 08.03.2021 | To implement e-invoicing for the taxpayers having aggregate turnover exceeding Rs. 100 Cr from 01st January 2021 To implement e-invoicing for the taxpayers having aggregate turnover exceeding Rs. 50 Cr from 01st April 2021 |
5. What are the advantages of e-invoice for businesses?
e-invoice has many advantages for businesses such as Auto-reporting of invoices into GST return, auto-generation of e-way bill (where required).
e-invoicing will also facilitate standardisation and inter-operability leading to reduction of disputes among transacting parties, improve payment cycles, reduction of processing costs and thereby greatly improving overall business efficiency.
6. What businesses need to do, to be e-invoice ready?
Businesses will continue to issue invoices as they are doing now. Necessary changes on account of e-invoicing requirement (i.e. to enable reporting of invoices to IRP and obtain IRN), will be made by ERP/Accounting and Billing Software providers in their respective software. They need to get the updated version having this facility.
7. Is an invoice/CDN/DBN (required to be reported to IRP by notified person), valid without IRN?
As per Rule 48(4), notified person has to prepare invoice by uploading specified particulars in FORM GST INV-01 on Invoice Registration Portal and after obtaining Invoice Reference Number (IRN).
As per Rule 48(5), any invoice issued by a notified person in any manner other than the manner specified in Rule 48(4), the same shall not be treated as an invoice.
So, the document issued by notified person becomes legally valid only with an IRN.
8. What documents are presently covered under e-invoicing?
i. Invoices
ii. Credit Notes
iii. Debit Notes,
when issued by notified class of taxpayers (to registered persons (B2B) or for the purpose of Exports) are currently covered under e-invoice.
Though different documents are covered, for ease of reference and understanding, the system is referred as ‘e-invoicing’.
9. What supplies are presently covered under e-invoice?
Supplies to registered persons (B2B), Supplies to SEZs (with/without payment), Exports (with/without payment), Deemed Exports, by notified class of taxpayers are currently covered under e-invoicing.
10. B2C (Business to Consumer) supplies can also be reported by notified persons?
No. Reporting B2C invoices by notified persons is not applicable/allowed currently.
11. Is e-invoicing applicable for NIL-rated or wholly-exempt supplies?
No. In those cases, a bill of supply is issued and not a tax invoice.
12. Whether the financial/commercial credit notes also need to be reported to IRP?
No, only the credit and debit notes issued under Section 34 of CGST/SGST Act have to be reported.
13. Whether e-invoicing is applicable for supplies by notified persons to Government Departments?
e-invoicing by notified persons is mandated for supply of goods or services or both to a registered person.
Thus, where the Government Department doesn’t have any registration under GST (i.e. not a ‘registered person’), e-invoicing doesn’t arise.
However, where the Govt. department is having a GSTIN (as entity supplying goods/services/ deducting TDS), the same has to be mentioned as recipient GSTIN in the e-invoice.
14. Whether e-invoicing is applicable for invoices between two different GSTINs under same PAN?
Yes. e-invoicing by notified persons is mandated for supply of goods or services or both to a registered person.
As per Section 25(4) of CGST/SGST Act, “A person who has obtained or is required to obtain more than one registration, whether in one State or Union territory or more than one State or Union territory shall, in respect of each such registration, be treated as distinct persons for the purposes of this Act.”
15. For high sea sales and bonded warehouse sales, whether e-invoicing is applicable?
No. These activities/transactions are neither supply of goods nor a supply of services, as per Schedule III of CGST/SGST Act.
16. What is the applicability of e-invoice for import transactions?
e-invoice is not applicable for import Bills of Entry.
17. For which entities/sectors, e-invoicing is not applicable / exempt?
a. Special Economic Zone Units
b. Insurers
c. Banking companies or financial institutions, including a non-banking financial company (NBFC)
d. Goods Transport Agency (GTA) supplying services in relation to transportation of goods by road in a goods carriage
e. Suppliers of passenger transportation service
f. Suppliers of services by way of admission to exhibition of cinematograph films in multiplex screens
g. Persons registered in terms of Rule 14 of CGST Rules (OIDAR)
18. The exemption from e-invoicing is w.r.t the nature of supply/transaction or w.r.t the entity?
It is with respect to the entity.
19. Do SEZ Developers need to issue e-invoices?
Yes, if they have the specified turnover and fulfilling other conditions of the notification.
In terms of Notification (Central Tax) 61/2020 dt. 30-7-2020, only SEZ Units are exempted from issuing e-invoices.
20. Are Free Trade & Warehousing Zones (FTWZ) exempt from e-invoicing?
Yes. As per Foreign Trade Policy, Free Trade & Warehousing Zones (FTWZ) are only a special category of Special Economic Zones, with a focus on trading and warehousing.
21. Is e-invoicing applicable for supplies by notified persons to SEZs?
Yes, e-invoicing is applicable for supplies by notified persons to SEZs.
In terms of Notification (Central Tax) 61/2020 dt. 30-7-2020, only SEZ Units are exempt from issuing e-invoices.
22. Our entity’s aggregate turnover had crossed the prescribed threshold during current financial year (e.g. during 2020-21). From what date, I’m supposed to start e-invoicing?
If your turnover exceeds the prescribed limit in the current financial year, then starting e-invoicing would be required w.e.f. beginning of next financial year.
In the example given, as you had crossed the threshold during 2020-21, e-invoicing will be applicable w.e.f. 1st April 2021.
23. Regarding the turnover threshold, the e-invoice notification mentions ‘aggregate turnover in any preceding financial year since 2017-18’. Considering GST was implemented since 1-7-2017, how to reckon ‘aggregate turnover’ for the FY 2017-18?
‘Aggregate Turnover’ has to be calculated as per the definition under Section 2(6) of CGST Act. Hence, for the Financial Year 2017-18, the ‘aggregate turnover’ has to be reckoned from 1-7-2017 till the end of FY.
24. There is an SEZ unit and a regular DTA unit under same legal entity (i.e. having same PAN). In one of the financial years since 2017-18, the aggregate total turnover of the legal entity is more than notified limit (considering both the GSTINs), however, the turnover of DTA unit is below notified limit.
In this scenario, as SEZ unit is exempt from e-invoicing, whether e-invoicing will be applicable to DTA Unit?
Yes, it will be applicable, because the aggregate turnover of the legal entity in this case exceeds the notified limit. The requirement is based on ‘aggregate turnover’ on the common PAN.
25. Is e-invoicing applicable to invoices issued by Input Service Distributor (ISD)?
No
26. Whether e-invoicing is applicable for supplies involving Reverse Charge?
If the invoice issued by notified person is in respect of supplies made by him but attracting reverse charge under Section 9(3), e-invoicing is applicable.
For example, a taxpayer (say, a Firm of Advocates having aggregate turnover in a FY is more than Rs. 500 Cr.) is supplying services to a company (who will be discharging tax liability as recipient under RCM), such invoices have to be reported by the notified person to IRP.
On the other hand, where supplies are received by notified person from (i) an unregistered person (attracting reverse charge under Section 9(4)) or (ii) through import of services, e-invoicing doesn’t arise / not applicable.
27. How to know a particular supplier is supposed to issue e-invoice (i.e. invoice along with IRN/QR Code)?
On fulfilment of prescribed conditions, the obligation to issue e-invoice in terms of Rule 48(4) (i.e. reporting invoice details to IRP, obtaining IRN and issuing invoice with QR Code) lies with concerned taxpayer.
However, as a facilitation measure, all the taxpayers who had crossed the prescribed turnover in a financial year from 2017-18 onwards have been enabled to report invoices to IRP.
One can search the status of enablement of a GSTIN on e-invoice portal: https://einvoice1.gst.gov.in/ > Search > e-invoice status of taxpayer
This listing of GSTINs is solely based on the turnover of GSTR-3B as reported to GST System. It may contain exempt entities or those for whom e-invoicing is not applicable for some other reason. So, it may be noted that enablement status on e-invoice portal doesn’t automatically mean that the taxpayer is supposed to do e-invoicing. If e-invoicing is not applicable to a taxpayer, they need not be concerned about the enablement status and may ignore it.
Further, the turnover slab of taxpayer can also be ascertained through “Search Taxpayer” / “Know Your Supplier” Sections on GST portal also.
In case any registered person, is required to prepare invoice in terms of Rule 48(4) but not enabled on the portal, he/she may request for enablement on portal: ‘Registration -> e-Invoice Enablement’.
28. Where can I get the list of all taxpayers who are required to issue e-invoice?
It is difficult to make precise list of taxpayers who are required to issue e-invoice, as the fulfilment of conditions prescribed for e-invoicing (e.g. crossing of turnover threshold, exemptions, nature of supplies made etc.) is dynamic in nature.
However, the list of GSTINs which are eligible and/or actually generating IRNs is published on IRP and updated on periodic basis. Please visit:
https://einvoice1.gst.gov.in/Others/GSTINsGeneratingIRN
Further, onus is on the concerned taxpayer to check the conditions and follow the law while the recipient shall confirm this fact with his suppliers, as the list may contain the names of exempt entities also but who might have been shown as enabled for e-invoice.
29. I am a buyer. For some of my suppliers, the status on IRP is shown as ‘enabled for e-invoice’. But, my supplier says that they are exempt from e-invoicing or that e-invoicing is not applicable for them (for some reason). What about this?
As already clarified in other FAQ, the enablement status on e-invoice portal doesn’t mean that a taxpayer is legally obligated to do e-invoicing.
The ‘enablement’ was to primarily ensure only the taxpayers having notified turnover limits (and not any taxpayer at their option) are able to register and test/report invoices on trial portal / IRP.
The listing of enabled GSTINs was solely based on the turnover criteria of GSTR-3B, as reported to GST System. So, it may contain those entities, depending on facts of a case, to whom e-invoicing might not be applicable for some reason. Thus, it is for the concerned taxpayer (both Buyers and Suppliers) to confirm fulfilment or otherwise of conditions as per notification/rules.
In case of any Doubt regarding Membership you can mail us at [email protected]
Join Studycafe's WhatsApp Group or Telegram Channel for Latest Updates on Government Job, Sarkari Naukri, Private Jobs, Income Tax, GST, Companies Act, Judgements and CA, CS, ICWA, and MUCH MORE!"