CBSE Class 12 Economics Syllabus 2022-23
CBSE Class 12 Economics Syllabus: CBSE Released Class 12 Economics Syllabus for the 2022-23 Term. Economics Syllabus includes National Income, Money and Banking, Determination of Income and Employment, Government Budget and the Economy, Balance of Payments, etc. Total Marks for Economics paper will be 100 and out of 100 80 Marks for Theory and 20 Marks for Project. Here is the detailed syllabus. The total Time for the Exam will be of 3 Hours. Economics Paper code is 030.
CBSE Class – 12
Economics (Code No. 030)
XII (2022-23)
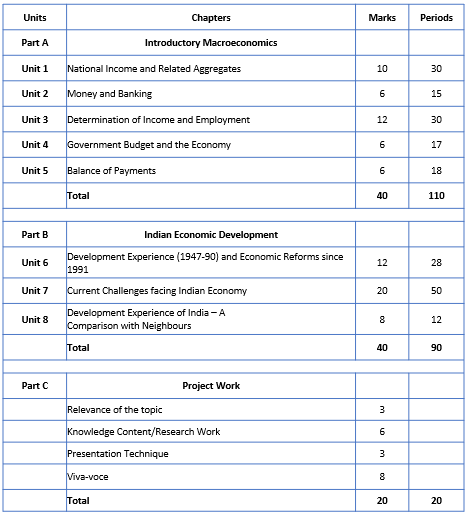
CBSE Class 12 Economics Syllabus 2022-23Part A: Introductory Macroeconomics (40 Marks)
Unit 1: National Income and Related Aggregates (10 Marks)
- What is Macroeconomics?
- Basic concepts in macroeconomics: consumption goods, capital goods, final goods, intermediate goods; stocks and flows; gross investment and depreciation.
- Circular flow of income (two-sector model); Methods of calculating National Income – Value Added or Product method, Expenditure method, Income method.
- Aggregates related to National Income:
- Gross National Product (GNP), Net National Product (NNP), Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and Net Domestic Product (NDP) – at market price, at factor cost; Real and Nominal GDP.
- GDP and Welfare
Unit 2: Money and Banking (6 Marks)
- Money – meaning and functions, supply of money – Currency held by the public and net demand deposits held by commercial banks.
- Money creation by the commercial banking system.
- Central bank and its functions (example of the Reserve Bank of India): Bank of issue, Govt. Bank, Banker’s Bank, Control of Credit through Bank Rate, CRR, SLR, Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate, Open Market Operations, Margin requirement.
Unit 3: Determination of Income and Employment (12 Marks)
- Aggregate demand and its components.
- Propensity to consume and propensity to save (average and marginal).
- Short-run equilibrium output; investment multiplier and its mechanism.
- Meaning of full employment and involuntary unemployment.
- Problems of excess demand and deficient demand; measures to correct them – changes in government spending, taxes and money supply.
Unit 4: Government Budget and the Economy (6 Marks)
- Government budget: meaning, objectives and components.
- Classification of receipts: revenue receipts and capital receipts;
- Classification of expenditure: revenue expenditure and capital expenditure.
- Balanced, Surplus and Deficit Budget: measures of government deficit.
Unit 5: Balance of Payments (6 Marks)
- Balance of payments account: meaning and components
- Balance of payments: Surplus and Deficit
- Foreign exchange rate: meaning of fixed and flexible rates and managed floating.
- Determination of exchange rate in a free market, Merits and demerits of flexible and fixed exchange rate.
- Managed Floating exchange rate system
Part B: Indian Economic Development (40 Marks)
Unit 6: Development Experience (1947-90) and Economic Reforms since 1991 (12 Marks)
- A small introduction of the state of Indian economy on the eve of independence.
- Indian economic system and common goals of Five Year Plans.
- Main features, problems and policies of agriculture (institutional aspects and new agricultural strategy), industry (IPR 1956; SSI – role & importance) and foreign trade.
Economic Reforms since 1991:
Features and appraisals of liberalisation, globalisation and privatisation (LPG policy); Concepts of demonetization and GST
Unit 7: Current challenges facing Indian Economy (20 Marks)
- Human Capital Formation: How people become resource; Role of human capital in economic development; Growth of Education Sector in India
- Rural development: Key issues – credit and marketing – role of cooperatives; agricultural diversification; alternative farming – organic farming
- Employment: Growth and changes in work force participation rate in formal and informal sectors; problems and policies
- Sustainable Economic Development: Meaning, Effects of Economic Development on Resources and Environment, including global warming
Unit 8: Development Experience of India: (8 Marks)
- A comparison with neighbours
- India and Pakistan
- India and China
- Issues: economic growth, population, sectoral development and other Human Development Indicators
Part C: Project in Economics (20 Marks)
- Relevance of the topic (3 Marks)
- Knowledge Content/Research Work (6 Marks)
- Presentation Technique (3 Marks)
- Viva-voce (8 Marks)
Click Here to Download the PDF
StudyCafe Membership
Join StudyCafe Membership. For More details about Membership Click Join Membership Button
Join MembershipIn case of any Doubt regarding Membership you can mail us at contact@studycafe.in
Join Studycafe's WhatsApp Group or Telegram Channel for Latest Updates on Government Job, Sarkari Naukri, Private Jobs, Income Tax, GST, Companies Act, Judgements and CA, CS, ICWA, and MUCH MORE!"

