Choosing between the old and new income tax regimes to reduce tax liability might be difficult for many taxpayers.
Reetu | Apr 19, 2024 |

New Vs Old Tax Regime: Which Tax Regime is Beneficial for Taxpayers in New Financial Year?
New Vs Old Tax Regime: Choosing between the old and new income tax regimes to reduce tax liability might be difficult for many taxpayers. It actually depends on how many deductions from the total income you can take to lower your taxable income.
You might make an easy decision if you know your gross total income and the lowest number of deductions required to pay the same amount of tax under each regime.
This is because the old tax regime would have been beneficial if you could deduct more than this amount, and the new tax regime would save you more money if you could deduct less than this minimum level.
Knowing the minimum deductions provides an individual with an idea of the tax regime that is most beneficial to them. This knowledge can be useful when deciding on a tax regime for TDS on Salary. When selecting a tax regime for TDS on salary, you would use an expected/estimated gross total income amount, and any deductions intended to be claimed would also be anticipated.
However, after the financial year has ended and the final data for income and deductions are available, detailed computations must be performed prior to picking a tax regime when completing the income tax return. When completing an income tax return, taxpayers have the option to modify the tax regime they previously selected.
Keep in mind that starting with the new financial year from 1st April 2024, the new income-tax regime is the default chosen regime. As a result, if you want to continue with the old tax regime, you must select it in your Income Tax Regime (ITR) or file Form 10 – IEA, if you have business income, when completing your return. Taxpayers who do not have company income will have the option of switching between regimes on a yearly basis.
All taxpayers are eligible for a basic income exemption of Rs.3 lakh under the new tax regime. It provides more income tax slabs with lower tax rates. Furthermore, a salaried individual can claim two deductions: Rs.50000 as a standard deduction from salary/pension income and an employer contribution to the NPS account of up to 10% of pay (14% for government employees) under the new tax regime.
Coming back to the comparison of both tax regimes, keep in mind that the minimum deductions that must be claimed in the old tax regime to ensure that the tax outgo is equal in both tax regimes are determined by income level.
View this post on Instagram
Old Tax Regime
Advantages
Deduction aplenty: Deduct various expenses such as investments in the Public Provident Fund (PPF), equity-linked savings scheme (ELSS), National Pension System (NPS) under Section 80C, House Rent Allowance (HRA), medical expenses under Section 80D, interest on home loan repayment, leave travel allowances (LTA), education loans (Section 80E), and more. These deductions significantly reduce your taxable income, resulting in lower tax liabilities.
Designed for investors and individuals with high expenses: If you invest extensively in some tax-saving tools, pay interest on a home loan, or incur significant medical bills, the old tax regime can provide significant tax benefits by lowering your taxable income.
Disadvantages
Higher rate of Tax Slabs: The old tax regime has higher tax slabs as compared to the new tax regime. This implies that even after claiming deductions if your income falls into a higher tax rate, you may end up paying more taxes.
Burden of Record-keeping: Maintaining complete and accurate records for all claimed deductions was essential under the old tax regime. This can be time-consuming and requires careful preparation throughout the year.
With the simpler approach, the new tax regime was introduced in 2020. The new tax regime simplifies the filing of taxes.
Advantages
Lower Rate of Tax Slabs: The new tax regime has a reduced tax rate slab as compared to the old tax regime. This can lead to lesser tax payments, particularly for persons in lower income levels.
Simpler filing of Taxes: Most expenses no longer require deductions under the new regime. This streamlines the tax filing process by eliminating the need to keep track of deductions.
Disadvantages
Less Number of Deductions: Unlike the old tax regime, the new regime allows for very few deductions. This can be problem-causing if you have significant investment, home loan interest payments, or substantial medical expenses.
Low flexibility: The lack of deductions in the new regime may limit your capacity to reduce your taxable income, perhaps resulting in greater tax liability for people who could have benefited more from deductions under the old regime.
1. Calculation of Taxable Income: Firstly, the taxpayer needs to calculate taxable income under both tax regimes – new and old. The new rule may favour people with fewer deductions and exemptions.
If your income is less than Rs.5 lakh, you are likely to pay no tax under either regime. However, if your income is higher, consider the possible tax savings from deductions under the old regime. You can use a tax calculator to determine your tax liability under both regimes. If your income exceeds Rs.10 lakh, the new regime may be simpler; but, the old regime may still provide significant tax savings through deductions.
2. Evaluate Exemptions and Deductions: If you have significant investments and expenses that qualify for deductions under the old tax regime (e.g., 80C, 80D, HRA), it may be more advantageous.
If you invest extensively in tax-saving instruments (such as PPF and ELSS), claim medical expenses, or pay interest on a home loan, the old tax regime may provide more tax benefits.
You decide how much time and work you want to put into filing taxes. The new regime is simpler, but may not provide the same degree of tax savings. The old regime allowed for more deductions but necessitated meticulous record-keeping.
3. Savings Vs Simplicity: The new regime is a bit simpler, but it may result in greater taxes if you have been actively claiming deductions and exemptions to decrease your taxable income.
4. Take into Account Future Financial Goals: If you are contemplating long-term savings or investments, the old tax regime may provide additional benefits due to deductions for such investments.
After the end of the financial year, you will need to compute your income and determine which regime will result in a lesser tax liability. As a result, you may choose your regime.
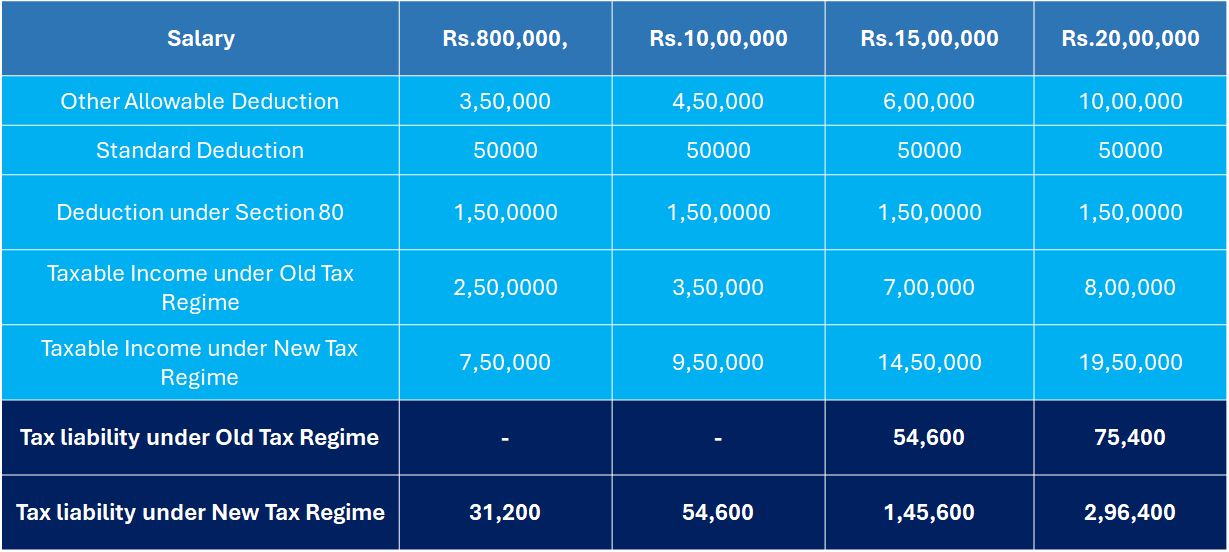
The table below displays four pay brackets: Rs 800,000, Rs 10,00,000, Rs 15,00,000, and Rs 20,000.
As can be seen, the taxable income under the new regime is always higher than the old regime for the same salary because the old regime provides for extra deductions in addition to the standard deduction.
In case of any Doubt regarding Membership you can mail us at [email protected]
Join Studycafe's WhatsApp Group or Telegram Channel for Latest Updates on Government Job, Sarkari Naukri, Private Jobs, Income Tax, GST, Companies Act, Judgements and CA, CS, ICWA, and MUCH MORE!"